Responsible AI in Every Classroom
The “Responsible AI in Every Classroom” curriculum integrates AI, data science, and coding with MIT App Inventor to give K-12 students starting their AI journeys a deeper and more holistic foundation in AI. Below, access the full “Responsible AI in Every Classroom” curriculum for free and join the Educator Collaborative mailing list to stay up to date with our latest professional development and curriculum offerings for teachers! Keep reading to learn more about our pedagogy, the curriculum, and its individual units in greater detail.
Note: All of our curriculum materials are free and open-source under CC BY-SA. However, please understand that we are a small team and do not have the bandwidth to offer individualized support. If you have questions or concerns, you may post in the MIT App Inventor Community Forum, where a number of App Inventor experts graciously volunteer their time to support the broader community. If you would like to partner with the App Inventor Foundation or sponsor teacher trainings for your school or program, please reach out to us via our contact form.
Overview
Alignment with UNESCO Guidelines
All units and learning activities are aligned with the UNESCO AI Competency Framework for Students—co-authored by Dr. Natalie Lao of the App Inventor Foundation—which articulates the UN’s guidelines for the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that K-12 students should acquire to understand and actively engage with AI in a safe and meaningful manner. It is organized into four aspects: Human-centred mindset, Ethics of AI, AI techniques & applications, and AI system design. Each unit of this curriculum is purposefully designed to address specific competency blocks within these domains, promoting a holistic and student-centered approach to AI education.
Additionally, this curriculum integrates the UNESCO Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence, which builds upon the foundational work of the UNESCO Beijing Consensus on Artificial Intelligence and Education. Together, these frameworks ensure that this curriculum not only builds technical understanding but also fosters responsible, ethical, and future-ready AI citizens.
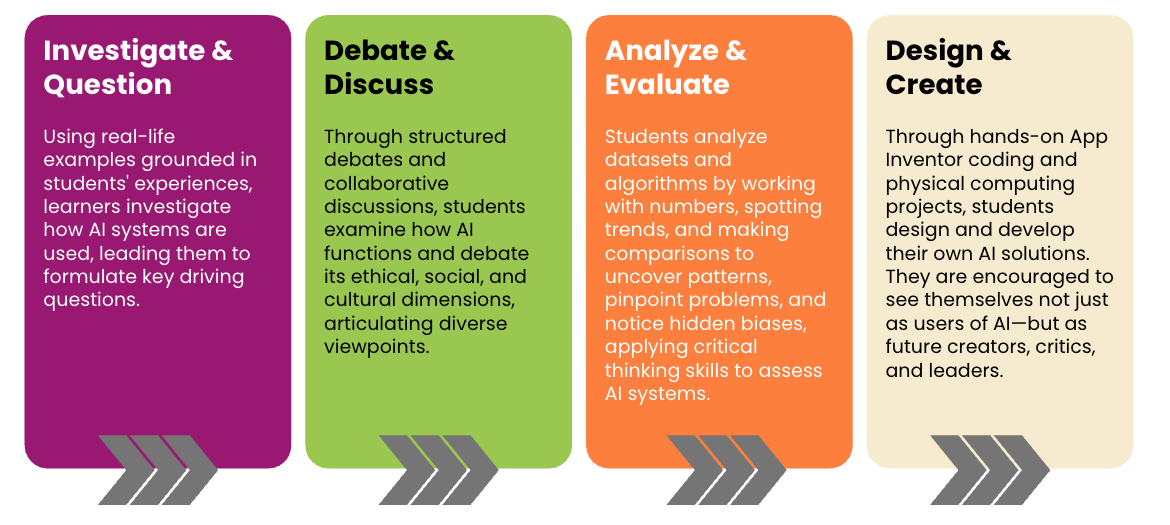
Lesson Structure
In every unit of the curriculum, students go through four iterative cycles: Investigate & Question, Debate & Discuss, Analyze & Evaluate, and Design & Create.
Guided by the above structure, students delve into the following application areas:
AI: Through case studies, debates, and hands-on development of AI applications, students critically examine algorithms and technologies from multiple perspectives, gaining a deeper understanding of both the benefits and potential drawbacks of AI.
Data science: Students apply statistics and data science to topics relevant to their lives, such as music, exams, and water quality. They will understand quantitatively how data and algorithms drive what we see and hear, and where biases may come from.
Coding with MIT App Inventor: Students learn to create with AI. They will feel confident in using generative AI, machine learning, and image classification to build an app that solves a problem relevant to their daily lives.
Ethics: Ethical considerations are embedded throughout the curriculum. When students use generative AI, they reflect on privacy, and when they study data, they examine issues of bias.
The Units
The first set of curriculum units in “Responsible AI in Every Classroom” is designed with a modular structure to support flexible implementation. Educators are encouraged to begin with Introducing AI, an engaging, unplugged activity that introduces students to the UN’s AI Ethics Principles. Through real-world news articles and peer-to-peer discussions, students explore the concept of being responsible digital citizens in the age of AI. Following this, four in-depth units can be taught in any order, each focusing on a distinct theme: Predicting Grades, Recommending Music, Telling Stories, and Protecting Water. These units align with different competency blocks from the UNESCO AI Competency Framework and include hands-on activities in data analysis and coding, fostering both technical and ethical understanding of AI.
The Intro Unit: Introduction to Responsible AI
Through a series of stimulating questions and fun quizzes, the unit introduces what AI is and why students should learn about it. Students also explore AI ethics through real-world AI in the news using jigsaw activities.
Sample activities:
Questions to spark interest
Fun debate to understand meaning of AI
Reading news articles and writing reflections to understand ethical isues
The Grades Unit: Using AI and Data Science to Predict Grades
Students critically examine AI's role in grading homework and exams through articles and debates. They then conduct statistical exercises to make predictions, realizing the limitations of data sets. This leads to a final reflection on what constitutes AI and human versus AI capabilities.
Sample activities:
Debate on whether AI can be used to give grades
Fun game: use mathematics and logical reasoning to find errors in a table of data
Group project: propose a solution or algorithm to deal with missing data
The Music Unit: Music Recommendation and Data
Students investigate recommendation algorithms, engaging directly with datasets to reveal embedded issues. Through a practical App Inventor project, they collect music preference data, ultimately cleaning and analyzing it to develop recommendations.
Sample activities:
Fun game: rate how danceable a song is vs Spotify to see subjectivity in data and algorithms
Students do music recommendation based on data in action
Group project: make an app to collect data, validate data and clean up messy data to make decisions while discussing fairness
The Stories Unit: Large Language Models and Generating Stories
Students will delve into the mechanics of how large language models (LLMs) comprehend meaning. Through a structured debate, they'll evaluate LLMs' strengths, weaknesses, limitations, and ethical implications, considering their societal impact. The curriculum also covers prompt engineering and culminates in students programming a fun app that uses an LLM to generate stories, while assessing potential ethical concerns arising from their creation.
Sample activities:
Use activities to understand how LLMs work
Game to experience good prompt engineering
Make an app that not only generates but also analyzes to discuss copyright and transparency
The Water Unit: Climate Change Happens Below Water
Students use App Inventor and Micro:bit to establish a system for collecting water quality data. They'll then analyze and visualize this data, subsequently employing AI to interpret the findings and research potential solutions.
Sample activities:
Use Micro:bit and sensor to collect data and use AI to interpret
Use Venn diagram to visualize information
Group project: design water treatment with the help of AI
Looking for the full Responsible AI in Every Classroom Curriculum? Download the materials here.
Interested in joining the Educator Collaborative mailing list? Sign up here.
Have questions about the curriculum? Post in the Community Forum.
Want to partner with us or sponsor a teacher training? Fill out our contact form.